If you are working on a text heavy document, or would like to make better use of your page by splitting it in half adding a column is your answer.
Columns split your page into a newspaper style layout, the text will run down two or three narrow columns which can be useful if you are trying to split your content across one page, create a flyer, brochure, report, step by step instructions or even a terms and conditions document.
Creating a table by highlighting rows and columns in Word 2019. Creating a table by highlighting rows and columns can be fast, but it limits the size of your table to a maximum of eight rows and ten columns. To create a table by highlighting rows and columns, follow these steps: Click the Insert tab. To do that, you have to insert a column break. You can insert a column break in one of two ways: Press CTRL-SHIFT-ENTER simultaneously; or Go to the Layout tab, click Breaks, and choose Column. Insert New Columns. If you need to add more details to each item in your table, you need to add more columns. Click inside an existing column. Click the Layout tab. To add a new column to the left of an existing column, click Insert Left. To add a new column to the right of an existing column, click Insert Right.
This article was written for users of Microsoft Word 2010. However, these steps will be very similar in other versions of Word as well. Step 1: Open the document in Word 2010 that contains the table that you want to modify. Step 2: Click inside a table cell in the column to the left of where you want to insert the new column.
When inserting a column, Microsoft will spit your page vertically with the text running down the first column before starting at the top of the second and so on.
In this post we will show you how to add one or multiple columns to your Microsoft Word document.
Adding a Column to your Word Document
- Open Microsoft Word
- Click the Insert Tab
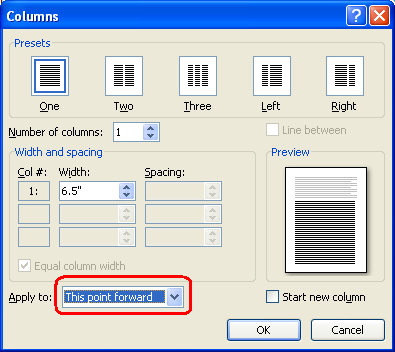
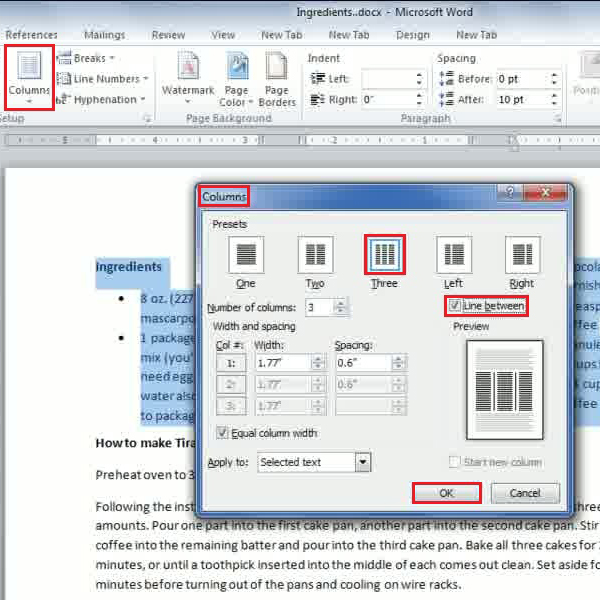
- Under the Insert Tab, Click Columns
- Select the number of Columns you would like to insert
Microsoft Word’s Column Options Explained
One, Two, Three will insert that number of even vertical columns into your document
Left, Right will insert a column smaller on the described side and larger on the other. For example, a Left column will create two columns with the left side covering around a quarter of your document leaving the right side covering the remaining space.
More Columns will give you the option to insert more than three columns and customise.
Looking for an easier way to Merge your Microsoft Word Documents together?
These days we are all about finding the most efficient way of doing things, from saving our eyes with dark mode so we can work without straining them to collaborating with your team on a Microsoft Word document without having to worry about merging two files together at the end.
It’s a simple ask, that Microsoft hasn’t quite solved for just yet.
Microsoft has a feature called ‘merge’ that shows you the differences between the two documents and allows you to manually pull across the accepted changes from each. Its a start, but it’s still fairly manual and can be time-consuming.
With that in mind, the smart guys over at Simul Docs – a very fancy new tool that makes collaborating in Word easy added a simple, merge feature to save you time.
Simul Docs will automatically pick up when two people are simultaneously working on the same document, create two new, separate versions for you, then flag with the document owner that there are now two versions that require their review before they can be merged.
See Simul won’t automatically merge the two files for you without asking, because it also knows you may not want to accept all of the changes in both. So it gives you the chance to run your eyes over both files, take as much or as little time as you like and then when you are happy – press merge. At the click of a button, you can merge the two documents back into one and continue collaborating with ease.
When you merge two documents in Simul, rest assured that all of the tracked changes, comments and fancy formatting will remain the same. Nothing will be lost during the process, unless of course you decided during your review process that you didn’t want to take that comment or change over in the merge. Its completely up to you!
Simul also offers some other pretty fancy features to help you collaborate such as version control, tracked changes, edits and comments, easy sharing and accessibility.
Because so many of us do find ourselves working offline, it’s important to Simul Docs that you can access and collaborate from anywhere, even where there isn’t a strong internet connection.
Simul is accessible from anywhere, if you are offline that’s ok, Simul will allow you to continue working as normal, with all of their nifty features and then the moment your device finds a connection Simul will update a live file and share it with the team.
With the ability to work offline, comes the risk of two or more team members working on the document at once without us knowing. Which is why the merge function exists, so you don’t have to worry about who is working when, or from where. Simul has you covered.
With Simul in your team, you can collaborate without concern. Knowing that Simul will have you covered, making merging, collaboration and working offline as easy as it should be.
Home > Articles > Operating Systems, Server > MAC OS X/Other
␡- Building a Table
How To Insert Columns In Word For Mac Free
This chapter is from the book
This chapter is from the book
Topics include the following:
- Inserting a table into a Word document
- Working with table rows and columns
- Adding and populating document headers and footers
- Choosing a page orientation and paper size
- Setting the page margins
- Adding footnotes and endnotes
In the previous chapter, you dealt with Word at the “tree” level of words, sentences, and paragraphs. But getting more out of Word also requires that you deal with the program at the “forest” level of pages and documents. This means you need to get familiar with Word’s page layout tools.
Page layout refers to how text and paragraphs are laid out on each page, and it involves building tables, adding headers and footers, setting margin sizes, specifying the page orientation, choosing the paper size, and so on. This chapter shows you how to work with these and other page layout features.
Building a Table
Most Word documents consist of text in the form of sentences and paragraphs. However, including lists of items in a document is common, particularly where each item in the list includes two or more details (which means a standard bulleted list won’t do the job). For a short list with just a few details, the quickest way to add the list to a document is to type each item on its own line and press Tab between each detail. You could then add tab stops to the ruler (see Chapter 4, “Working with Text in Word”) to line up the subitems into columns.
That works for simple items, but to construct a more complex list in Word, you can build a table, a rectangular structure with the following characteristics:
- Each item in the list gets its own horizontal rectangle called a row.
- Each set of details in the list gets its own vertical rectangle called a column.
- The rectangle formed by the intersection of a row and a column is called a cell, and you use the table cells to hold the data.
In other words, a Word table is similar to an Excel worksheet or an Access datasheet.
Insert a Table
Although Word gives you no less than one-half dozen ways to build a table, you need to know only the most straightforward method.
- Position the insertion point where you want the table to appear.
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click Table.
Click Insert Table to display the Insert Table dialog.
- Specify the number of columns you want in your table.
- Specify the number of rows you want in the table.
Click OK. Word inserts the table.
- Position the insertion point inside a cell and then add the text that you want to store in the cell. Repeat for the other cells in the table.
- Click the Layout tab.
Use the Table Column Width box to set the width of the column.
Select Table Elements
Before you can change the layout or formatting of a table, you need to select the part of the table you want to work with. Here are the techniques to use (note that, in each case, “Layout” refers to the table’s Layout tab, which appears to the right of the Table Design tab):
- Select a cell—Select the cell and then click Layout, Select, Select Cell (or triple-click anywhere in the cell).
- Select two or more adjacent cells—Select the top-left cell you want to include in the selection, then drag the mouse down and to the right to include the other cells.
- Select a row—Click any cell in the row and then click Layout, Select, Select Row.
- Select two or more adjacent rows—Select at least one cell in each row and then click Layout, Select, Select Row.
- Select a column—Click any cell in the column and then click Layout, Select, Select Column.
- Select two or more adjacent columns—Select at least one cell in each column and then click Layout, Select, Select Column.
- Select the entire table—Click any cell in the table and then click Layout, Select, Select Table.

Format a Table
To change the formatting of the table cells, you select the cells you want to work with and then use Word’s standard formatting tools (font, paragraph, and so on). For more table-specific formatting, you can use the Table Design tab.
- Click inside the table.
- Click the Table Design tab.
Click the More button of the Table Styles gallery.
Click the style you want to apply to the table.
- Click Header Row to toggle header formatting on and off for the first row. For example, in some styles the first row is given darker shading, top and bottom borders, and a bold font.
- Click Total Row to toggle total formatting on and off for the bottom row.
- Click Banded Rows to toggle alternating formatting for all the rows.
- Click First Column to toggle special formatting on and off for the first column.
- Click Last Column to toggle special formatting on and off for the last column.
Click Banded Columns to toggle alternating formatting for all the columns.
- Select the cells you want to format and then use the Shading gallery to click a background color.
Select the cells you want to format and then use the Border Styles gallery to click a border style.
Word Insert Column
Insert New Rows
There are times when you need to add more data to a table. Word provides several tools that enable you to expand a table. If you’re adding new items to the table, you need to add more rows.
To add a new row at the end of the table, position the insertion point in the lower-right cell—that is, the last column of the last row—and press Tab.
- Click the Layout tab.
- To add a new row above an existing row, position the insertion point inside the existing row and then click Insert Above.
To add a new row below an existing row, position the insertion point inside the existing row and then click Insert Below.
Insert New Columns
If you need to add more details to each item in your table, you need to add more columns.
- Click inside an existing column.
- Click the Layout tab.
- To add a new column to the left of an existing column, click Insert Left.
To add a new column to the right of an existing column, click Insert Right.
Delete Table Elements
How To Add A Column In Word
If you no longer need a part of your table—for example, a cell, a row, or a column—you can delete it. You can delete multiple cells, rows, or columns, and, if necessary, you can delete the entire table.
Select the table element you want to delete.
- Click the Layout tab.
- Click Delete.
Click the command that represents the type of table element you want to delete. If you click the Delete Cells command, the Delete Cells dialog opens. The path to love deepak chopra.
- Click whether you want to shift the remaining cells to the left or up, or if you would rather delete the entire row or column.
Click OK.
Related Resources
- Online Video $239.99
- Online Video $239.99
How To Insert Columns In Word For Mac Os

How To Insert Columns In Word For Mac Download
- Online Video $239.99
